[Python] Data Class Builder: collections.namedtuple, typing.NamedTuple, @dataclass
Data Class Builder란?
데이터(lat, lon)를 저장하는 역할만을 수행하는 단순한 클래스 Coordinate를 생각해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
class Coordinate:
def __init__(self, lat, lon):
self.lat = lat
self.lon = lon
moscow = Coordinate(55.756, 37.617)
이렇게 단순히 생성한 Coordinate 클래스는 다음과 같은 단점을 가진다.
object로부터 상속받은__repr__는 object의 주소를 반환하기 때문에, 다음과 같이 객체 자체를 출력해서 확인할 때 유용하지 않다.1 2
moscow # <__main__.Coordinate at 0x10662f0d0>
object로부터 상속받은__eq__는is와 동일하게 object ID를 비교하므로==연산자로 클래스 내 필드를 비교할 수 없으며, 두Coordinate를 비교하려면 각 attribute에 대해 모두 comparison을 진행해야 한다.1 2
moscow == Coordinate(lat=55.756, lon=37.617) # False
이러한 단점들로 인해, 간단히 데이터를 담기 위한 용도의 클래스를 생성할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있는 data class builder가 등장하였다.
위의 Coordinate 클래스를 세 가지 data class builder인 collections.namedtuple, typing.NamedTuple, @dataclass를 이용한 방법으로 바꾸어보고, 각각의 특징에 대해 알아보도록 하자!
[1] collections.namedtuple
1
2
3
4
from collections import namedtuple
Coordinate = namedtuple('Coordinate', 'lat lon')
moscow = Coordinate(55.756, 37.617)
__repr__가 저장된 데이터의 값을 보여주므로 유용하다.1 2
moscow # Coordinate(lat=55.756, lon=37.617)
__eq__또한 저장된 각 attribute의 값을 비교하므로==가 meaningful 하다.1 2
moscow == Coordinate(lat=55.756, lon=37.617) # True
tuple의 subclass인 class를 생성한다.1
issubclass(Coordinate, tuple)
[2] typing.NamedTuple
1
2
3
4
5
6
from typing import NamedTuple
# 다음의 두 가지 형태가 모두 가능하다.
Coordinate = NamedTuple('Coordinate',
[('lat', float), ('lon', float)])
Coordinate = NamedTuple('Coordinate', lat=float, lon=float)
- 기본적인 특징은
collections.namedtuple과 동일하다. class statement로도 사용할 수 있다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
class Coordinate(NamedTuple): lat: float lon: float def __str__(self): ns = 'N' if self.lat >= 0 else 'S' we = 'E' if self.lon >= 0 else 'W' return f'{abs(self.lat):.1f}°{ns}, {abs(self.lon):.1f}°{we}' moscow = Coordinate(55.756, 37.617) print(moscow) # 55.8°N, 37.6°E
tuple의 subclass이지만NamedTuple의 subclass가 아니다.1 2
issubclass(Coordinate, NamedTuple) # -- TypeError: issubclass() arg 2 must be a class, a tuple of classes, or a union
get_type_hints()함수로 타입 힌트를 확인할 수 있다.1 2 3 4
from typing import get_type_hints # type hint를 확인할 수 있다. get_type_hints(Coordinate)
[3] @dataclass
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# class statement example
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Coordinate:
lat: float
lon: float
def __str__(self):
ns = 'N' if self.lat >= 0 else 'S'
we = 'E' if self.lon >= 0 else 'W'
return f'{abs(self.lat):.1f}°{ns}, {abs(self.lon):.1f}°{we}'
- inheritance나 metaclass와 관련이 없는 class decorator 이다.
- 상속을 받지 않으므로
object의 subclass이다. frozen=True는 해당 instance가 변경될 수 없다는 것을 나타낸다.
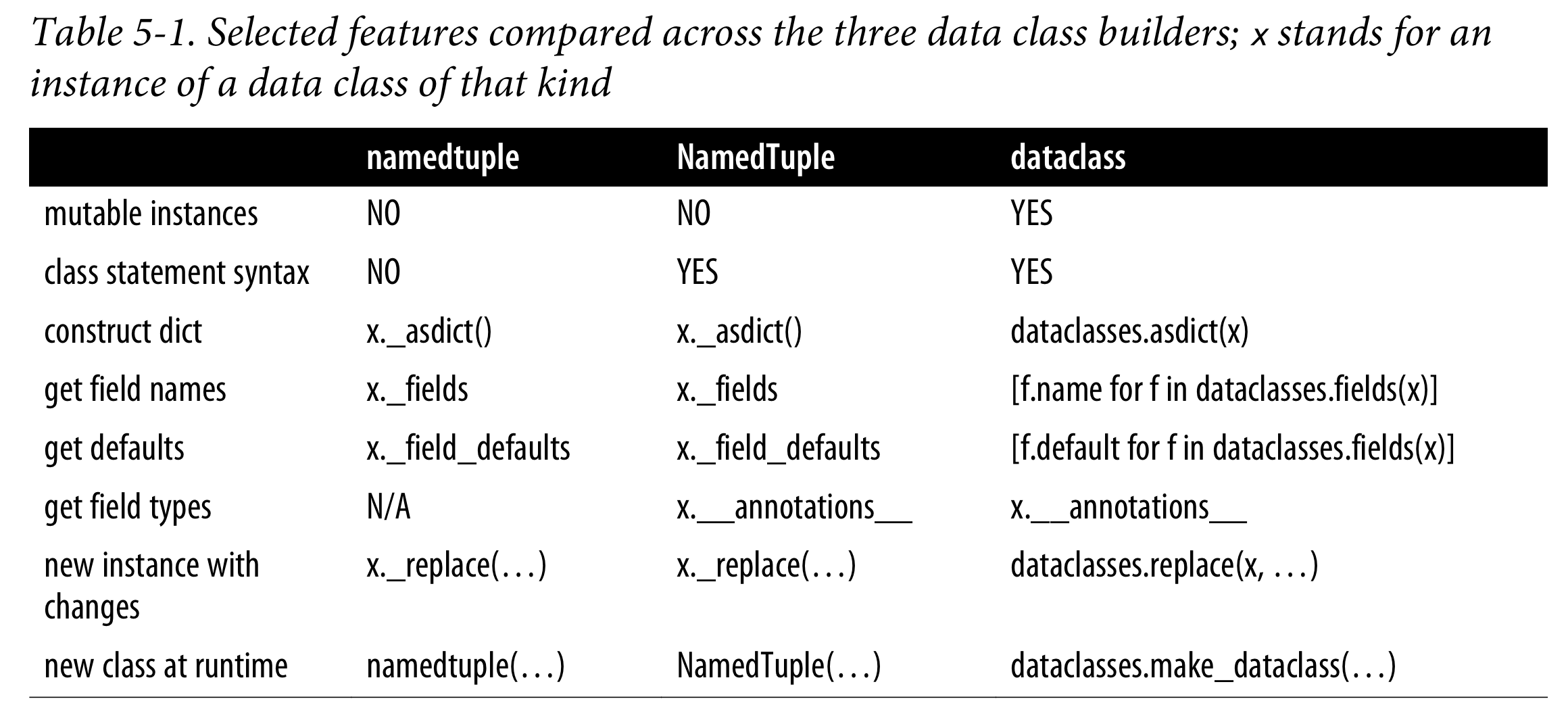
세 가지 Data Class Builder 비교
References
- “Fluent Python (2nd Edition)”, Ch05. Data Class Builders