[Python] First-Class Object, Higher-Order Function, 그리고 함수형 프로그래밍
TL;DR 📌
- 파이썬에서 모든 함수는 first-class object이다. 따라서 함수를 어떤 변수에 할당할 수 있으며, 그 변수로 호출할 수 있다. 그리고 함수를 다른 함수에 인자로 전달할 수도 있고, 어떤 함수의 결과로서 반환할 수도 있다.
- higher-order function이란 함수를 인자로 받거나 함수를 반환하는 함수(ex.
map,sorted,min,max등)를 의미하며, 프로그래밍 언어에 국한되는 개념이 아니다. lambda키워드를 통해 익명 함수를 편리하게 생성할 수 있으며, 이렇게 생성한 익명 함수는 higher-order function의 인자로 사용할 수 있다.- 파이썬에서는 first-class function과 여러 패키지(ex.
operator,functools)를 통해 함수형 프로그래밍을 시도할 수 있다.
1. First-Class Object의 조건
파이썬에서 “모든 함수는 first-class object” 라는 말을 한 번 쯤 들어본 적이 있을 것이다. 과연 first-class object 란 무엇일까?
어떤 객체가 다음의 조건들을 만족할 때, 그 프로그램 엔티티는 first-class object라고 한다.
- 런타임에 생성된다.
- 변수나 자료구조 내의 원소에 할당된다.
- 함수에게 인자로서 전달된다.
- 함수의 결과로서 반환된다.
2. First-Class Function
파이썬에서 모든 함수는 first-class object이기 때문에 함수를 “first-class function”이라 부를 수 있다.
함수를 first-class object로 가지는 것은 함수형 언어의 핵심적인 특징이지만, 그 유용함 때문에 함수형 언어가 아닌 JavaScript, Go, Java 등에서도 채택하고 있다고 한다.
다음의 예시 factorial 함수를 통해 first-class function의 특징을 살펴보자.
1
2
3
def factorial(n):
"""returns n!"""
return 1 if n < 2 else n * factorial(n - 1)
함수를 어떤 변수에 할당할 수 있으며, 그 변수로 호출할 수 있다.
1 2 3 4 5
fact = factorial print(fact) # <function factorial at 0x10501e200> print(fact(5)) # 120
다른 함수(ex.
map(func, iter))에 인자로 전달할 수 있다.1 2 3 4
print(map(factorial, range(11))) # <map object at 0x105026680> print(list(map(fact, range(11)))) # [1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880, 3628800]
3. Higher-Order Function
first-class function은 프로그래밍 언어에서의 함수에 국한된 개념이라면, higher-order function(고차 함수)은 일반적인 함수에도 적용 가능한 개념이다.
higher-order function이란, 함수를 인자로 받거나 함수를 반환하는 함수를 의미한다.
파이썬에서는 대표적으로 map, sorted, min, max 등의 함수가 higher-order function에 속한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
fruits = ["strawberry", "fig", "apple", "cherry", "raspberry", "banana"]
sorted(fruits, key=len)
# ['fig', 'apple', 'cherry', 'banana', 'raspberry', 'strawberry']
def reverse(word):
return word[::-1]
sorted(fruits, key=reverse)
# ['banana', 'apple', 'fig', 'raspberry', 'strawberry', 'cherry']
3-1. Higher-Order Function을 현대적인 방법으로 대체하기
higher-order functions 중
apply,map,filter,reduce는 다음의 코드로 대체 가능하다.
[1] apply
apply는 Python 2.3에서 deprecated 되었고, Python 3에서는 제거되었다.다음과 같이 그냥 함수를 실행하면 된다.
1
fn(*args, **kwargs)
[2] map, filter
- 두 함수 모두 여전히 Python 3에서도 built-in으로 지원되지만, list comprehensions와 generator expressions로 대체 가능하다.
map,filter는 Python 2에서는 list를, Python 3에서는 generator를 반환한다. 따라서 각 버전의 가장 적절한 대체제는 각각 list comprehension와 generator expression이다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7
list(map(factorial, range(6))) [factorial(n) for n in range(6)] # -- map -> list comprehension # [1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120] list(map(factorial, filter(lambda n: n % 2, range(6)))) # -- map & filter [factorial(n) for n in range(6) if n % 2] # -- map & filter -> list comprehension # [1, 6, 120]
[3] reduce
reduce의 동작
- series에서 연속적으로 등장하는 아이템에 대해 동일한 연산을 적용한다.
- 이전 결과들을 누적한다.
- 값의 series를 하나의 값으로 reduce 한다.
- Python 2에서는 built-in이었으나, Python 3에서는
functools모듈로 이동했다. sum1 2 3 4
from functools import reduce from operator import add reduce(add, range(100)) == sum(range(100))
all(iterable): iterable 안에 falsy element가 없으면True를 반환한다.any(iterable): iterable 안에 하나의 element라도 truthy 하면True를 반환한다.
3-2. 익명 함수와 lambda 키워드
lambda키워드는 익명 함수(anonymous function)를 만드는 데에 유용하게 사용된다.lambda함수의 내부는 pure expression이어야 한다.pure expression이란?
- 다른 파이썬 statement(ex.
while,try,=등)을 포함하면 안 된다. - assignment expression인
:=은 사용 가능하나, 코드가 너무 복잡해지고 가독성이 떨어지므로def를 사용한 regular function으로 refactor 되어야 한다.
- 다른 파이썬 statement(ex.
higher-order function의 인자로 사용하기 편리하다. 새로운 function을 정의하지 않아도 되기 때문이다.
1 2 3 4
fruits = ["strawberry", "fig", "apple", "cherry", "raspberry", "banana"] sorted(fruits, key=lambda word: word[::-1]) # -- reversed # ['banana', 'apple', 'fig', 'raspberry', 'strawberry', 'cherry']
lambda는 함수의 인자로 사용하지 않는 경우를 제외하면 unreadable 또는 unworkable 하므로, 이러한 경우가 아니라면defstatement를 이용한 function definition으로 refactor 하는 것을 권장한다.lambdaexpression은defstatement와 동일하게 function object를 생성한다. (syntactic sugar)
4. 함수형 프로그래밍과 파이썬
4-1. 함수형 프로그래밍 (Functional Programming)
프로그래밍 패러다임은 크게 명령형과 선언형으로 나뉜다.
명령형 패러다임(imperative programming): 어떻게(“
HOW”) 할 것인지에 집중한다.절차형 프로그래밍, 객체지향형 프로그래밍
선언형 패러다임(declarative programming): 무엇을(“
WHAT”) 할 것인지에 집중하고, 어떻게 할 것인지는 컴퓨터에게 위임한다.함수형 프로그래밍, 논리형 프로그래밍
함수형 프로그래밍은 선언형 패러다임에 해당하는 것으로, 간단히 말하면 문제를 함수들의 집합으로 분해하고 상태와 가변 데이터를 멀리하는 패러다임이다.
4-2. 파이썬에서 함수형 프로그래밍을 지원하는 방법
관련 공식 문서
파이썬의 first-class function과 pattern matching, 그리고 여러 패키지(ex. operator, functools) 덕분에 함수형 프로그래밍 스타일을 파이썬에도 도입할 수 있다.
[1] operator 모듈
operator에서 제공하는 함수를 이용하면lambda와 같은 trivial functions를 작성할 필요가 없다.
mul1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
from functools import reduce from operator import mul def factorial_trivial(n): return reduce(lambda a, b: a * b, range(1, n + 1)) def factorial(n): return reduce(mul, range(1, n + 1)) # -- lambda 함수를 operator의 mul 함수로 대체
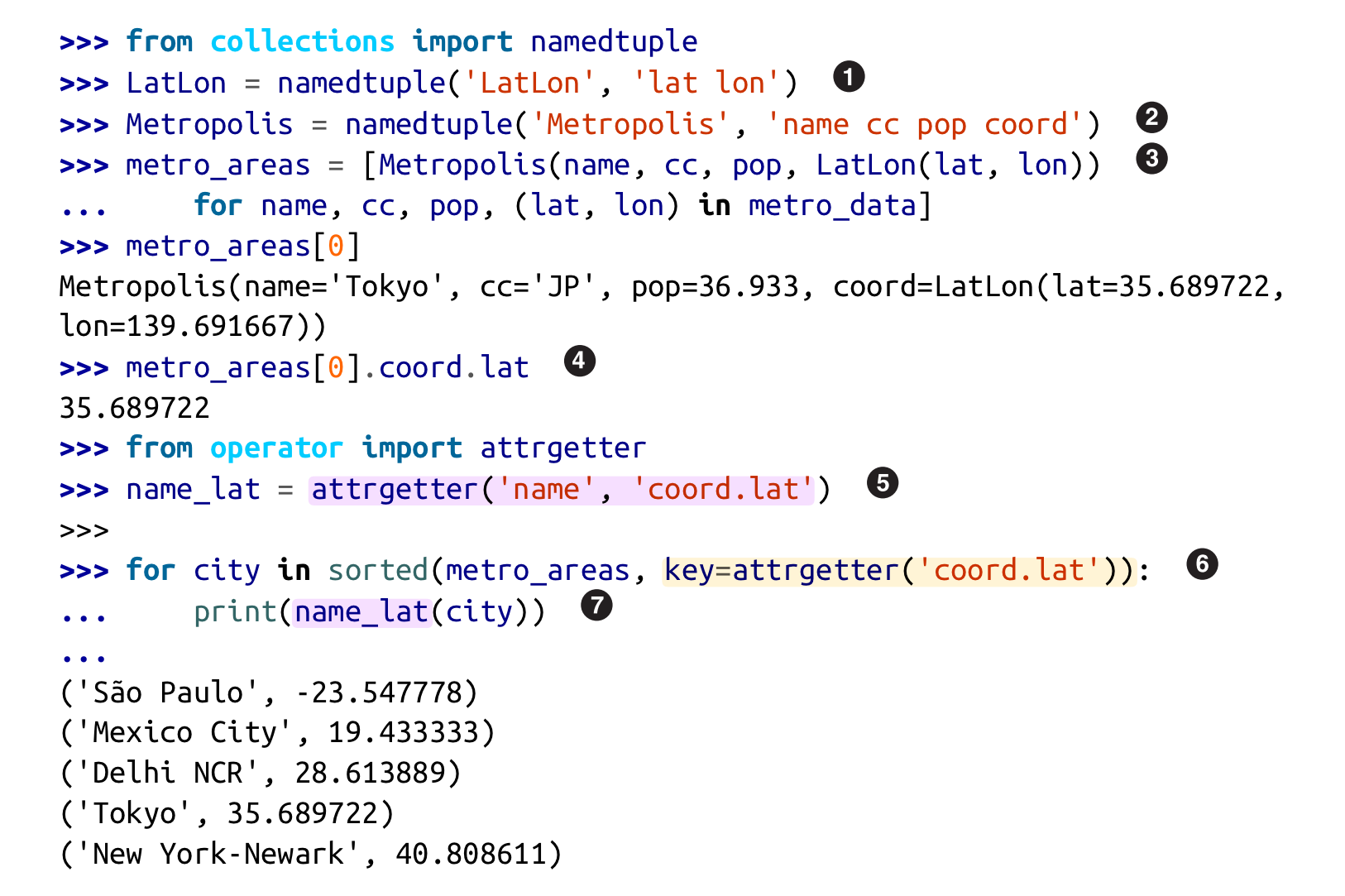
itemgetter: creates functions to extract object attributes by indexattrgetter: creates functions to extract object attributes by name- multiple attribute name arguments를 전달하면 tuple로 결과를 반환한다.
- argument name에
.이 포함된 경우(ex.coord.lat), nested object를 navigate하여 해당 attribute를 찾는다.
methodcaller: calls a method by name on the object given as argumentf = methodcaller('name')다음의f(b)호출은b.name()을 반환한다.다음의 경우에는
str.upper(s)처럼 사용해도 된다.1 2 3 4 5 6
from operator import methodcaller s = "The time has come" upcase = methodcaller("upper") upcase(s) # == s.upper() # 'THE TIME HAS COME'
일부 arguments를 freeze 하는 partial application도 가능하다.
1 2 3
hyphenate = methodcaller("replace", " ", "-") # -- partial application to freeze some arguments hyphenate(s) # == s.replace(" ", "-") # 'The-time-has-come'
operator내의 주요 function listaugmented assignment operators (ex.
iadd==+=,iand==&=)
- first argument가 mutable한 경우, first argument를 in place로 바꾼다.
- 아닌 경우,
iprefix가 없는 function처럼 동작하여 operation 결과를 반환한다.
[2] functools.partial
원본 callable의 인자 중 일부를 predetermined values로 설정한 새로운 callable을 반환한다. 따라서 더 적은 수의 인자로 callable을 호출할 수 있다.
first argument로 callable을 받고, 이후에는 positional / keyword arguments를 받는다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
from operator import mul
from functools import partial
triple = partial(mul, 3)
print(triple(7))
# 21
print(list(map(triple, range(1, 10))))
# [3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
picture = partial(tag, "img", class_="pic-frame") # -- positional & keyword argument
print(picture(src="wumpus.jpeg"))
# <img class='pic-frame' src='wumpus.jpeg' />
print(picture)
# functools.partial(<function tag at 0x107e928c0>, 'img', class_='pic-frame')
print(picture.func)
# <function tag at 0x107e928c0>
print(picture.args) # -- positional argument
# ('img',)
print(picture.keywords) # -- keyword argument
# {'class_': 'pic-frame'}
예를 들어, 여러 언어의 text를 다룰 때, unicode.normalize("NFC", s) 를 functools.partial을 이용하여 간편하게 사용할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import unicodedata, functools
nfc = functools.partial(unicodedata.normalize, "NFC")
s1 = "café"
s2 = "cafe\u0301"
print(s1, s2) # café café
print(s1 == s2) # False
print(nfc(s1) == nfc(s2)) # True
functools module의 다른 기능으로는 다음과 같은 것들이 있다.
| 함수 | 설명 |
|---|---|
functools.partialmethod | partial과 동일한 동작을 method에 대해 수행한다. |
cache, singledispatch 등 | function decorator로 사용된다. |
References
- “Fluent Python (2nd Edition)”, Ch07. Functions as First-Class Objects
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10141124/any-difference-between-first-class-function-and-high-order-function
- https://medium.com/@la.place/higher-order-function-이란-무엇인가-1c61e0bea79
- https://jongminfire.dev/함수형-프로그래밍이란
- https://medium.com/@lazysoul/함수형-프로그래밍이란-d881230f2a5e
- https://velog.io/@kyusung/함수형-프로그래밍-요약
- https://evan-moon.github.io/2019/12/15/about-functional-thinking/
- https://iosdevlime.tistory.com/entry/CSBasic-좀-더-나은-프로그램을-위해-프로그래밍-패러다임